Received- January 20, 2020; Accepted- March 3, 2020
International Journal of Biomedical Science
16(1), 1-4, Mar 15, 2020
© 2020 John Thomas Palathingal et al. Master Publishing Group
Interpretation of Safety and Efficacy of Hydroxychloroquine Alone and Along with Methotrexate Combination in Rheumatoid Arthritis
John Thomas Palathingal1, Divya Miryala2, Goverdhan Reddy Puchchakayala2, Swathi Thomas2, Venkatswami3
1 Department of Clinical Pharmacology, HCG Cancer Hospital Gulbarga, India;
2 Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Vaagdevi College of Pharmacy, Kakatiya University, MGM Hospital, Hanamkonda, Telangana, India;
3 Department of Orthopaedics, Kakatiya Medical College, Mahathma Gandhi Memorial Hospital, Warangal, Telangana, India
Corresponding Author: Dr. JOHN THOMAS PALATHINGAL, Clinical Pharmacologist, HCG Cancer Centre, Health Care Global Enterprises, Kalburagi, Karnataka- 585102, INDIA. Tel: +919791140261; E-mail: johnpt1993@gmail.com.
Financial support and sponsorship: Nil
|
|
ABSTRACT
 |
BACKGROUND: Several drugs for rheumatoid arthritis are available. Comparative studies of treatment with Hydroxychloroquine (against Methotrexate) reported a better quality of life. AIM: The study was designed to evaluate safety and efficacy of patient with rheumatoid arthritis when treated as combination therapy of Methotrexate and Hydroxychloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine alone, a Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatoid Drug (DMARD). MATERIAL AND METHODS: This was a prospective observational study which was conducted in rheumatology department in a tertiary care Hospital, Warangal, India. Patients who were diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis as per Guidelines of American College of Rheumatology aged between 18 and 60 years were recruited. First group patient were treated with Hydroxychloroquine 400 mg and second group patient were treated with combination of Methotrexate 7.5 mg and Hydroxychloroquine 400 mg. Simple Disease Activity Index criteria of improvement according to disease activity score 28 was considered as the primary efficacy variable. The Baseline and end of study values were evaluated. RESULT: After 3 months, improvement was noted in patient treated with Methotrexate and Hydroxychloroquine combination when compared to Hydroxychloroquine mono therapy alone. There was statistical significance in improvement of disease activity between the two groups (P = 0.02). CONCLUSION: The study concluded Methotrexate and Hydroxychloroquine combination therapy is more effective to Hydroxychloroquine therapyalone in efficacy of reducing disease activity in the treatment of severe rheumatoid arthritis.
KEY WORDS:
Hydroxychloroquine, Methotrexate, SDAI Score, Rheumatoid Arthritis
|
|
INTRODUCTION |
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that mainly affects joints. It is the most common autoimmune disorder in which the body mistakenly attack joint as foreign substance like bacteria &viruses. The inflammation of synovial (tissue that lines the joints) results in swelling and pain in and around the joint (1-3). Rheumatoid arthritis affect joint of hand, feet, wrist, elbow, knees, and ankles. Joint deformities are usually symmetrical. If unchecked it can damage cartilage, the elastic tissue, and bones itself which cannot be reversed. Nearly 1.5 million people in U. S have Rheumatoid arthritis. Women are usually suffering 3 times / folds than that of men. Rheumatoid arthritis commonly starts between age 30-60years,whereas in men it may occur later in life (3-5). This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of Hydroxychloroquine alone and with combination of Methotrexate for the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, which help in determining effect of Hydroxychloroquine Monotherapy in active RA. To minimize the progression of the problems associated with the existing condition (7-10).
|
|
MATERIALS AND METHODS |
The present study is a prospective observational study, which was conducted during the period February to October 2017 at rheumatology in a tertiary care hospital Warangal India accordance with declaration of Helsinki following approval of Institutional Ethics Committee. Patient history was taken and examination was performed. Female patient between the age group of 18 and 60 years with active rheumatoid arthritis were recruited according to American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria. Patients with impaired kidney function, bone marrow insufficiency, uncontrolled hypertension, pregnant or lactating patients and those who desired to become pregnant in 2-3 months were not included in study. One twenty-eight patients were divided into two groups, in which first group patients were given Combination therapy and second group patients were given Mono therapy. Patients were explained about the study & informed consent taken by explaining them in their local language. Institutional Human Ethical Committee approved after submission of protocol and IHEC No. was MGM /VCOP/PHARMD/V/O2/2017. Patients were assessed for severity of disease with European league Against Rheumatism (EULAR) and score was calculated by simplified disease activity index (SDAI). The Haematological and clinical adverse events were the secondary parameters. SDAI was calculated using the following formula: Total SDAI [0-86] is equal to sum of Tender joint score [0-28], Swollen joint score [0-28], Patient global score [0-10], Provider global score [0-10] and C-reactive protein{mg/dl}[0-10].The score of SDAI indicates the current activity of the rheumatoid arthritis. Patients with SDAI score of [0.0-3.3] were considered with Remission, [3.4-11.0] Low activity, [11.1-26.0] Moderated activity and [26.1-86.0] High activity. At, last the improvement in disease activity is measured by calculating the difference in SDAI score.
First grouppatients received combination of drug, namely Methotrexate 7.5mg/week/oral and tablet Hydroxychloroquine 400mg/daily/oral. Group 2 received tablet Hydroxychloroquine 400mg/daily/oral. Dose escalation was not done as the addition of Hydroxychloroquine reduced the dose of Methotrexate and effect starts after 6-12weeks. Haematological Parameter like red blood cell, white blood cell,Haemoglobin, platelet count, creatinine, aspartate aminotransferases and alanine aminotransferases, Blood pressure was recorded at the baseline.
|
|
STATISTICAL METHODS |
The statistical analysis of data was done by statistical software namely SPSS 20.0 version and Microsoft Excel 2010 followed by unpaired t-test p<0.05 value is considered as significant results were expressed as Mean ± SD.
|
|
RESULTS |
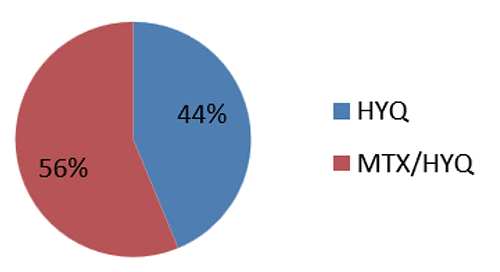
128 Patients wererecruited, according to ACR criteria that conformed to EULAR with SCORE (≥ 6). Figure 1 shows 128 patients 56 were treated with (Hydroxychloroquine 400 mg) and remaining 72 patients were treated with (Hydroxychloroquine 400 mg and Methotrexate 7.5 mg). The distribution of subjects was even between the age limit in the study (Figure 2).
The demographic base line did not change between the two groups. There is significant improvement in number of patients with combination therapy when compared to mono therapy. Changes in Disease activity was reduced after 3 months in both groups, statistical significance was seen in both groups (Figure 3, Table 1).
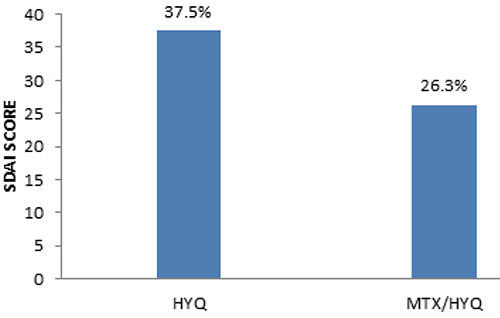
According to graph combination therapy show better action then a mono therapy, Decrease in score indicate better action in both combination. Both drug show fluctuation in the graph.
The clinical side effects were secondary parameters one subject was presented with vomiting and liver failure was withdrawn from the study, as the plasma liver enzyme were elevated (SGOT 1450IU & SGPT 1330IU). There was no much variation in liver enzyme among other patient with combination therapy and monotherapy. Hematological parameters were assessed after 3months were also within normal limits in both the groups. The most commonly seeing side effects were nausea and vomiting. Hydroxychloroquine and Methotrexate therapy show greater efficacy when compared with Hydroxychloroquine therapy alone in active rheumatoid arthritis Figure 4.
View larger version :
[in a new window] |
Figure 1. Drug distribution among patients. MTX, Methotrexate; HYQ, Hydroxychloroquine.
|
|
View larger version :
[in a new window] |
Figure 4. Simple Disease Activity Score. MTX, Methotrexate; HYQ, Hydroxychloroquine.
|
|
|
|
DISCUSSION |
This study was designed to evaluate the efficacy of combination therapy of Methotrexate and Hydroxychloroquine with monotherapy in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis over a period of three month. With the disease –modifying therapy currently available, complete remission of rheumatoid arthritis or disappointingly rare, Therefore,” most clinician have restored to using combination therapy of drug to treat a substantial subgroup of patients. There are few data to suggest that combination of drug is better than therapy with single drug. The study has highlighted the improvement in disease activity score in group one and group two by 3.04 and 3.06 respectively. Combination therapy showed significance which is below 0.05 i.e., 0.02 when compared to monotherapy. The study showed that the combination therapy is equivalent to mono therapy in improving hepatic safety profile. Hematological parameter illustrated no change. In addition treatment for severe active rheumatoid arthritis with combination of Methotrexate and Hydroxychloroquine is economical and can be considered effective and safe option in Indian population against Hydroxychloroquine. Based on our study we have concluded that combination therapy is more effective than mono therapy which is comparative to the study done by Shashikumar et al. in which they have documented that combination therapy of Methotrexate and Hydroxychloroquine is more effective than Leflunomide (6).
|
|
CONCLUSION |
Rheumatoid arthritis is crucial public health- related problem particularly in people after 30-35years on comparison with other age group due to, change in the lifestyle. However, risks are associated with hydroxychloroquine when continuous usage alone. In, few studies combination therapy show equal or better efficacy than single therapy. But with above result and discussion we conclude that hydroxychloroquine therapy show greater efficacy when compared with combination therapy in severe active rheumatoid arthritis.
|
|
FINANCIAL SUPPORT AND SPONSORSHIP |
Nil.
|
|
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST |
The authors declare that no conflicting interests exist.
|
|
ETHICAL STATEMENT |
Our study is involving human beings conducted in accordance with the principles of Declaration of Helsiniki and the guidelines on Good clinical practice.

|
(2)
| |
|
|
REFERENCES |
- Heijde Dv., Schiff M, Tanaka Y, et al. Correction: Low rates of radiographic progression of structural joint damage over 2 years of baricitinib treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open. 2019; 5 (2): e000898corr1.
- Bathon M, Martin JW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser RR, et al. A Comparison of Etanercept and Methotrexate in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2000; 343: 1586-1593.
- Felson D, Anderson J, Meenan R. Use of short-term efficacy/toxicity tradeoffs to select second-line drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. A metaanalysis of published clinical trials. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 1992; 35 (10): 1117-1125.
- Gossen N, Jacob L, Kostev K. Second-line therapy with biological drugs in rheumatoid arthritis patients in German rheumatologist practices: a retrospective database analysis. Rheumatology International. 2016; 36 (8): 1113-1118.
- Miwa Y, Isojima S, Saito M, Ikari Y, et al. Comparative Study of Infliximab Therapy and Methotrexate Monotherapy to Improve the Clinical Effect in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Internal Medicine. 2016; 55 (18): 2581-2585.
- Shashikumar N, Shivamurthy M, Chandrashekara S. Evaluation of efficacy of combination of methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine with leflunomide in active rheumatoid arthritis. Indian Journal of Pharmacology. 2010; 42 (6): 358.
- van Dongen H, van Aken J, Lard L, Visser K, et al. Efficacy of methotrexate treatment in patients with probable rheumatoid arthritis: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 2007; 56 (5): 1424-1432.
- Kalden J, Schattenkirchner M, Sörensen H, Emery P,. The efficacy and safety of leflunomide in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: A five-year followup study. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 2003; 48 (6): 1513-1520.
- O'Dell J, Haire C, Erikson N, Drymalski W, et al. Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Methotrexate Alone, Sulfasalazine and Hydroxychloroquine, or a Combination of All Three Medications. New England Journal of Medicine. 1996; 334 (20): 1287-1291.
- Paulus H, Egger M, Ward J, James Williams H. Analysis of improvement in individual rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, based on the findings in patients treated with placebo. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 1990; 33 (4): 477-484.